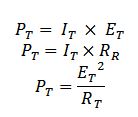Multi-tester (VOM-volt/ohmeter) also called
multimeter is designed to measure different magnitudes of electrical units:voltage,current and resistance. It incorporates the functions of a voltmeter,ohmmeter,and Milli-ammeter into one device. A multimeter maybe
Digital (DVOM/DMM) or
Analog.
Parts and functions of multi-tester
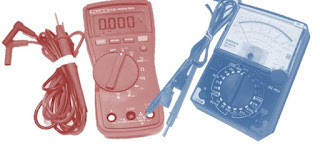 |
| Digital multimeter Analog multimeter |
1. Zero ohm adjuster- for analog multi-testers this part sets the indicator of the left scale to zero
2. Range Selector switch knob-this is a switch that is calibrated to select the proper range of the meter
3. Amperage terminal -plug in connection for red (positive) test lead for measuring amperes
4 +V.Ω.f terminal(positive )- terminal for positive test probe.It is used for most types of measurements.
5. -COM terminal (negative,N)- a terminal for the negative test probe
6. Home plate-Serves as the cover or panel for multi-tester
7. Indicator pointer- It deflects a certain point and use as a reference of where to read the measurement
8. Output socket- used for measuring special purpose such as high AC voltage,intensity of sounds in decibel,etc
9. Range Scale- it indicates the test function and scale option
10. Display for Digital multi meter(DMM) -it displays the measurement reading. Usually have a four digit display with a +/- indicator.
Preliminary setup before measurement
1. Before start measuring, make sure that the pointer stays at zero(0) position on the left end of the scale. If not,gently adjust the zero corrector with the use of screwdriver to set it to zero.
2.Select the proper range before measuring. Do not attempt to switch the range knob while measuring. Disconnect the test leads first before switching the range knob as it may damage your multimeter. in determining a measuring range,select a higher voltage than the value to be measured as well as where the pointer of the meter moves to considerable extent. however,select the maximum range and measure in case the extent of value to be measures can not be predicted.
Precautions for safety measurement
1. Never use meter on the electric circuit that exceeds 3k VA.
2. Pay special attention when measuring the voltage of AC30 volts or DC60V or more to avoid injury.
3. Never apply an input signals exceeding the maximum rating input value.
4. Never use meter for measuring the line connected with equipment that generates induced or surge voltage since it may exceed the maximum allowable voltage.
5. Never use meter if the meter or test leads are damaged or broken.
6. Never use encase meter.
7. Be sure to use fuse of the specified rating type.never use substitute of the use or never make a short circuit of the fuse.
8. Always keep your fingers behind the finger guards on the probe when making measurements.
9. Be sure to disconnect the test pins from the circuit when changing the function of the range.
10. Before starting measurement,make sure that the function and range are properly set in accordance with the measurement.
11. Never use meter with wet hands or in damp environment.
12. Never open tester case except when replacing batteries or fuses. Do not attempt any alteration of original specifications.
13. Never use test leads other than the specified test leads.
14. To ensure safety and maintain accuracy,calibrate and check the meter at least once a year.