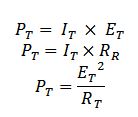Power dissipated by each individual resistance is simply added to find the total power dissipated by the series circuit. This same procedure also applies to parallel circuits. If there are five resistive branches in a parallel circuit and each was dissipated 1 watt of power, the total power the circuit is 5 watts . The individual power dissipations of all resistors are added to find the total power dissipated.
Pt= P1+P2+P3....+Pn
Pt=1W+1W+1W+1W+1W=5W
power Calculations in parallel Circuits
Where: I-current
E-voltage
R-Resistance
As an alternative method ,If you have already calculated the total or main line currents flowing in the circuits, the total circuit voltage,and /or the total circuit resistance, you can calculate the total power the circuit dissipates by using the three formulas listed above on the total circuit quantities.
where:
It-total current
Et-Total voltage
Rt-Total Resistance
Pt-Total power
Pt= P1+P2+P3....+Pn
Pt=1W+1W+1W+1W+1W=5W
power Calculations in parallel Circuits
Where: I-current
E-voltage
R-Resistance
As an alternative method ,If you have already calculated the total or main line currents flowing in the circuits, the total circuit voltage,and /or the total circuit resistance, you can calculate the total power the circuit dissipates by using the three formulas listed above on the total circuit quantities.
where:
It-total current
Et-Total voltage
Rt-Total Resistance
Pt-Total power