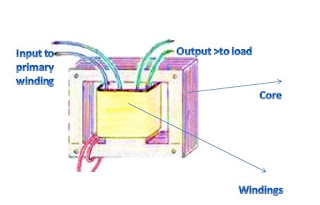
Transformer: Basic operation and construction
Transformer is an electrical device that converts voltage from one value to another that is, either from high voltage to lower voltage which is termed step- down transformer, or from lower voltage to higher voltage which is termed step up transformer.
The principle behind lowering or raising the voltage is done through magnetic induction between its coils. Changing current in the primary winding creates alternating magnetic field in its the core. And as the core multiplies this field and couples the most of the flux through the secondary transformer windings, It creates an induction of alternating voltage or the electromotive force in each of the secondary coil.
A transformer is constructed with the following essential parts :
1. Core (iron core or air core)
2. Windings ( primary winding or secondary winding)
3. Insulation (major insulation and minor insulation)
The core is made up of of lamination sheets. one of the best used as core is silicon steel
These sheets has its purpose:
a) to hold the windings in place
b) to serve as path for magnetic circuit or magnetic field
The lamination sheets are pressed tightly together leaving no spaces between sheets.
Another essential part of the transformer are the windings. Windings are made up of copper wire generally termed as magnetic wires. These wires are usually covered with varnish insulation. Other magnetic wires beside the varnished insulation are still covered with cotton and generally used for big transformer.
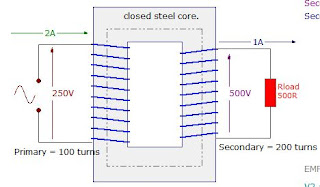 Windings are composed of primary and the secondary winding. The primary winding is the one that is connected to the power supply , the purpose of which is to get the required power. On the other hand, the secondary winding is the one connected to load and deliver the needed power. The secondary maybe one or more windings.
Windings are composed of primary and the secondary winding. The primary winding is the one that is connected to the power supply , the purpose of which is to get the required power. On the other hand, the secondary winding is the one connected to load and deliver the needed power. The secondary maybe one or more windings.
The insulation is used to separate or insulate iron core as well as the windings. There are two types of insulation used in transformer,
a.) major insulation
b) minor insulation. the major insulation is used to insulate or separate the windings from the iron core and insulate or separate the primary winding from the secondary winding. The minor insulation on the other hand is used to insulate or separate one layer of turns to the next layer.
Transformer Operation
When the primary winding is plugged or connected to the power source, magnetic lines of force are developed around the windings and travels within the iron core. By electromagnetic induction principle, these magnetic lines of force travelling around the core induces another voltage to the secondary windings which gives the idea although the primary and the secondary windings are separated or not connected to each other, a lower or higher voltage can be produced in the secondary winding. in this operation of transformer, one must recall his knowledge of the principles of electromagnetic induction.
Sources
Transformer is an electrical device that converts voltage from one value to another that is, either from high voltage to lower voltage which is termed step- down transformer, or from lower voltage to higher voltage which is termed step up transformer.
The principle behind lowering or raising the voltage is done through magnetic induction between its coils. Changing current in the primary winding creates alternating magnetic field in its the core. And as the core multiplies this field and couples the most of the flux through the secondary transformer windings, It creates an induction of alternating voltage or the electromotive force in each of the secondary coil.
 |
2. Windings ( primary winding or secondary winding)
3. Insulation (major insulation and minor insulation)
The core is made up of of lamination sheets. one of the best used as core is silicon steel
a) to hold the windings in place
b) to serve as path for magnetic circuit or magnetic field
The lamination sheets are pressed tightly together leaving no spaces between sheets.
Another essential part of the transformer are the windings. Windings are made up of copper wire generally termed as magnetic wires. These wires are usually covered with varnish insulation. Other magnetic wires beside the varnished insulation are still covered with cotton and generally used for big transformer.
 Windings are composed of primary and the secondary winding. The primary winding is the one that is connected to the power supply , the purpose of which is to get the required power. On the other hand, the secondary winding is the one connected to load and deliver the needed power. The secondary maybe one or more windings.
Windings are composed of primary and the secondary winding. The primary winding is the one that is connected to the power supply , the purpose of which is to get the required power. On the other hand, the secondary winding is the one connected to load and deliver the needed power. The secondary maybe one or more windings.The insulation is used to separate or insulate iron core as well as the windings. There are two types of insulation used in transformer,
a.) major insulation
b) minor insulation. the major insulation is used to insulate or separate the windings from the iron core and insulate or separate the primary winding from the secondary winding. The minor insulation on the other hand is used to insulate or separate one layer of turns to the next layer.
Transformer Operation
When the primary winding is plugged or connected to the power source, magnetic lines of force are developed around the windings and travels within the iron core. By electromagnetic induction principle, these magnetic lines of force travelling around the core induces another voltage to the secondary windings which gives the idea although the primary and the secondary windings are separated or not connected to each other, a lower or higher voltage can be produced in the secondary winding. in this operation of transformer, one must recall his knowledge of the principles of electromagnetic induction.
Sources