Alternator coil connections
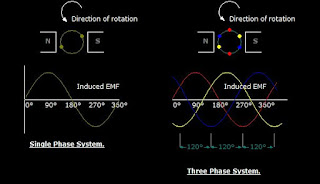
There are two ways of connecting the coils of the three phase AC generators or alternator in a load. These are the wye or the star connection and the delta connection. Generally, generators are wye connected ( earth wire) but loads can be either delta or wye.
1. Star Connected, 4-wire Alternator
iA

iC
iB
![]() This takes advantage of the fact that the sum of the three phase current is zero
This takes advantage of the fact that the sum of the three phase current is zero
iA +iB iC =0
When the generator has a balanced output and the loads connected to each phase are identical then the calculation of the voltages and current for, say the red phase can be applied equally to two other phases. The voltage in A,B,C are called phase voltages and are the potential difference developed between Vab, Vbc, Vac
2. Delta connected, 3-wire Alternator
In this configuration the connection has no neutral line. The voltage between pair of lines are equal to the phase voltage of the generator and the line current is the difference between the two phase currents.
The line currents are the currents flowing into and from the load where the actual current is the addition of the two.
For balanced poly-phase systems phases have identical line voltages and currents.

iA
iB
iC
 This takes advantage of the fact that the tree phase voltages always sum up to zero
This takes advantage of the fact that the tree phase voltages always sum up to zero
Va+Vb+Vc=0
Sources
Electrical engineering training series :Three phase alternator connection
Network analysis 2007
There are two ways of connecting the coils of the three phase AC generators or alternator in a load. These are the wye or the star connection and the delta connection. Generally, generators are wye connected ( earth wire) but loads can be either delta or wye.
1. Star Connected, 4-wire Alternator
iA

iC
iB
iA +iB iC =0
When the generator has a balanced output and the loads connected to each phase are identical then the calculation of the voltages and current for, say the red phase can be applied equally to two other phases. The voltage in A,B,C are called phase voltages and are the potential difference developed between Vab, Vbc, Vac
2. Delta connected, 3-wire Alternator
In this configuration the connection has no neutral line. The voltage between pair of lines are equal to the phase voltage of the generator and the line current is the difference between the two phase currents.
The line currents are the currents flowing into and from the load where the actual current is the addition of the two.
For balanced poly-phase systems phases have identical line voltages and currents.

iA
iB
iC
 This takes advantage of the fact that the tree phase voltages always sum up to zero
This takes advantage of the fact that the tree phase voltages always sum up to zeroVa+Vb+Vc=0
Sources
Electrical engineering training series :Three phase alternator connection
Network analysis 2007