Electrical Design of UCM Fellowship Hall-Makati City
Friday, March 31, 2017
Electrical Design for Bioregen Euro Warehouse
Electrical Design for Bioregen Euro Warehouse-400sm.
MEP Projects for SSA Architecture-Small Studio Associates
MEP Projects for SSA Architecture-Small Studio Associates, LLC, Las Vegas, NEVADA
-
MEP Design for DRIP Doctors Office-4050 Dean Martin Drive, Las Vegas Nevada
-
MEP Design for The IV District Doctors Office-2240 Village Walk Drive, Henderson NV
98052
Electrical Design of Temporary Facility for Alaska Milk Corporation
Electrical Design of Temporary Facility and Laboratory
Design of Gridtie Solar PV System for ALPROPS Management Inc.
Design and Installation of 30kW Gridtie Solar PV System in Centennial Garden Laguna
Design and Instrallation of 100kW Gridtie Solar PV System in Sariaya Resort with NET Metering
Design and Instrallation of 100kW Gridtie Solar PV System in Sariaya Resort with NET Metering
MEPF Works for NEWSIM Building Roof top Enclosure
Electrical, Plumbing and Fire Protection Works for NEWSIM Building Roof top Enclosure.
Electrical and Plumbing works for proposed Renovation of 2 Storey Building in Singian St. Makati City
Electrical and Plumbing works for proposed Renovation of 2 Storey Building in Singian St. Makati City
Supply and Installation Solar Street Light for Alscom Inc.
Supply and Installation of two (2) pieces of Solar Street Light and CCTV System for Alscom Inc. at 2053 Edison Street, Barangay San Isidro Makati City.
Grounding System Design for Chemical Charter and Coating Corporation
Supply and Installation of Industrial Fan for Ventilation System and Grounding System Design for Electric
Static Discharge for Chemical Charter and Coating Corporation located at Mercedez Ave. Pasig City
Sunday, September 18, 2016
Plant Design: Motor Protection Parameters
The table below is an example of a working protection parameters of an electrical system. A parameter sheet such as this will enable the designer to tabulate necessary initial values and calculations.
First is to work out in calculating the circuit current of a three phase motor circuit:
Circuit Current=kW/(√3∗kV∗pf )
Instrument and protection CTs are governed by standard IEC 60044-1 . The matching of CTs with protection relays calls for a thorough knowledge of CTs. The following section gives a few reminders in determining the CT ratio, the table below will give the recommended primary CT ratio for various circuit current in the motor protection section. See (link) for complete list of CT ratio per application.
CT Primary=kW/(√3∗kV∗pf *η )
If you do not know exact values for ϕ and η as a first approximation, you can assume that: cos ϕ = 0.8 ; η = 0.8. T. The secondary circuits of a CT must be suitable for the constraints related to its application for or protection purposes.
CT Secondary
For use in a local situation Isn = 5 A
For use in a remote situation Isn = 1 A
The use of 5 A in a remote situation increase the cross section of the line or the sizes of the transformer (lost in line). IEEE C57.13 Table 8 - Standard multi-ratio current transformer taps gives the standard ratings for instrument transformers. Sequence CT Ratio are constant 100/1 in 4.160 and 6.9kV Circuit.
For the circuit Type in 6.9kV , there are two recommended circuit types. Use Vacuum Circuit when the Current reached above 100 Amps or Fused Contractor when dealing with currents below 100 Amps.
NO.
|
Equipment
name
|
Nominal
power
(kW)
|
Circuit
calculation current(A)
|
CT
trans. ratio
|
Zero
sequence CT trans. ratio
|
Circuit
type
|
1
|
Motor Pump No.1
|
3400
|
355.6
|
1000/1
2000/1(Differential)
|
100/1
|
Vacuum
breaker
|
2
|
Motor Pump No.3
|
1400
|
146.4
|
500/1
|
100/1
|
Vacuum
breaker
|
3
|
Motor Pump No.3
|
1000
|
104.6
|
400/1
|
100/1
|
Vacuum
breaker
|
4
|
Motor Pump No.4
|
400
|
41.8
|
200/1
|
100/1
|
F-C
circuit
|
5
|
Motor Pump No.5
|
900
|
94.1
|
300/1
|
100/1
|
F-C
circuit
|
6
|
Motor Pump No.6
|
710
|
74.3
|
200/1
|
100/1
|
F-C
circuit
|
First is to work out in calculating the circuit current of a three phase motor circuit:
Circuit Current=kW/(√3∗kV∗pf )
Instrument and protection CTs are governed by standard IEC 60044-1 . The matching of CTs with protection relays calls for a thorough knowledge of CTs. The following section gives a few reminders in determining the CT ratio, the table below will give the recommended primary CT ratio for various circuit current in the motor protection section. See (link) for complete list of CT ratio per application.
CT Primary=kW/(√3∗kV∗pf *η )
If you do not know exact values for ϕ and η as a first approximation, you can assume that: cos ϕ = 0.8 ; η = 0.8. T. The secondary circuits of a CT must be suitable for the constraints related to its application for or protection purposes.
CT Secondary
For use in a local situation Isn = 5 A
For use in a remote situation Isn = 1 A
The use of 5 A in a remote situation increase the cross section of the line or the sizes of the transformer (lost in line). IEEE C57.13 Table 8 - Standard multi-ratio current transformer taps gives the standard ratings for instrument transformers. Sequence CT Ratio are constant 100/1 in 4.160 and 6.9kV Circuit.
For the circuit Type in 6.9kV , there are two recommended circuit types. Use Vacuum Circuit when the Current reached above 100 Amps or Fused Contractor when dealing with currents below 100 Amps.
Sunday, September 4, 2016
Power System Study for CADPI
Our freelancer have been involved in the Analysis of Electrical System of Central Azucarera De Don Pedro (CADPI) in Nasugbu , Batangas Philippines. The scope of the projects includes Short Circuit Analysis, Load Flow and Protective Device Coordination evaluation of the Plant.
Electrical Designs for Penthouse in Baguio City
Electrical Design for 4 Storey Residential/Commercial Building with Roof deck, Villanueva Residence-2 Storey Residential with Penthouse (Baguio City) and Manager’s Project : 2 Storey with Penthouse (Baguio City) . This is still on going project
Electrical Design Projects in USA
Our freelancer have handled major electrical design projects for clients in USA. Among these projects are design contracts under MR Engineering Consultants:
1. RECOVERY CAFE-FIRST CHRISTIAN CHURCH
80 South 5th Street, San Jose CA 95112
2.HOTEL CLARIANA-5 Storey Commercial Building
100 East Sta. Clara, & 10S 3rd St. San jose CA. 95113
3.North Bascom- Medical Office
105 North Bascom Ave. #100 & 101 San Jose CA
4. Elite Educational Institution
155 Anza St. Fremont CA
5. St. Martin of Tours
200 O' Conner Dr. San Jose CA
1. RECOVERY CAFE-FIRST CHRISTIAN CHURCH
80 South 5th Street, San Jose CA 95112
2.HOTEL CLARIANA-5 Storey Commercial Building
100 East Sta. Clara, & 10S 3rd St. San jose CA. 95113
3.North Bascom- Medical Office
105 North Bascom Ave. #100 & 101 San Jose CA
4. Elite Educational Institution
155 Anza St. Fremont CA
5. St. Martin of Tours
200 O' Conner Dr. San Jose CA
Electrical Design for ME Sikat Construction Corporation
Our engineer has undergone Electrical Design of Transmission Line for a temporary facility for ME Sikat Construction Corporation. The project also includes Electrical and Plumbing Design for Ground Floor and Mezzanine of Quezon Hall U.P Diliman Campus and Asian Institute of Tech Vldg UP AIT Diliman, U.P Diliman Campus.
Additional Projects:
1. Electrical Design of Transmission line project Temporary Facility.
1. Electrical Design of Transmission line project Temporary Facility.
(Finished 1.11.17)
Electrical redesign for Cement Manufacturer Association of the Philippines
Our Freelancer worked on the Electrical redesign of the building of Cement Manufacturer Association of the Philippines. The design works includes the details for installation of the grounding system and rewiring of tapping to Genset. The project was successfully closed on July 2016.
Saturday, September 3, 2016
Design and Analysis of PowerMount Comm. Structures
Design and Analysis of PowerMount Comm. Structures for T-Mobile of MDL Engg Soln Inc. a client from USA.
Monday, June 13, 2016
Generator excitation control operation
Increasing the output voltage of a generator is achieved by adjusting the magnitude of the excitation current. This
happens because as DC current is increased, the rotating magnetic field increases thereby increasing the generator voltage induced in the stator conductor. As the voltage is increased, the generator will transfer more MVAR into the power system.
Instead of collector rings, suppose that a brushless generator above is used in our example. The exciter is provided from the DC winding which is wound in the stator. The rotor produces ac current that is feed into the rectifier built in the shaft. The rectifier converts AC to DC and feed the rotor windings.
To control of the rectifier output in the field windings of the excitation generator, voltage regulator receives its command signal from the AC voltage controller which monitors the ac voltage of the monitor.
The limitation of the generator due to current in the stator should follow within the machine capability curve. Increasing the excitation current of the generator to deliver MVAR will produce heating in rotor winding. alternatively, if the excitation is reduced voltage and VARS will fall. then the machine will have weak magnetic field .
In the capability curve, the horizontal axis is the reactive power in per unit quantity, where 1 pu =159 MVAR and the vertical axis is the active power per unit quantity.
Instead of collector rings, suppose that a brushless generator above is used in our example. The exciter is provided from the DC winding which is wound in the stator. The rotor produces ac current that is feed into the rectifier built in the shaft. The rectifier converts AC to DC and feed the rotor windings.
To control of the rectifier output in the field windings of the excitation generator, voltage regulator receives its command signal from the AC voltage controller which monitors the ac voltage of the monitor.
The limitation of the generator due to current in the stator should follow within the machine capability curve. Increasing the excitation current of the generator to deliver MVAR will produce heating in rotor winding. alternatively, if the excitation is reduced voltage and VARS will fall. then the machine will have weak magnetic field .
 |
| Technical Data for Generator 60WX18Z-090 with Static Excitation 158,8 MVA 13800 V 60 Hz p.f. = 0,85 Tcg = 33 °C Temp.-Cl. = 130(B |
Monday, April 2, 2012
EEWeb Website of the Day April 2, 2012
This blog is featured in EEWeb - Electrical Engineering Community, as website of the day for April 2, 2012. This is an excellent recognition from a popular electrical engineering community website for hardware engineers. I'm happy and honored that this blog was on the front page of the EEweb and was included in the list of impressive websites that EEweb has recognized in the past.
Thank you EEWeb!
Update: 2013
The old name of this website was "Mathematics and Engineering Topics" and now changed to "EngineerMaths.com". The change was due to transfer of this website from free domain to a premium domain name. Every articles and feeds will be automatically redirected into our new domain. For example, when you visit our old address [Mathematics and Engineering Topics], it will redirect you to our new address.
Thank you EEWeb!
Update: 2013
The old name of this website was "Mathematics and Engineering Topics" and now changed to "EngineerMaths.com". The change was due to transfer of this website from free domain to a premium domain name. Every articles and feeds will be automatically redirected into our new domain. For example, when you visit our old address [Mathematics and Engineering Topics], it will redirect you to our new address.
 |
| Screenshot of Enginering and Mathematics Topics in EEweb |
 |
| Screenshot of EEweb home page |
Wednesday, March 28, 2012
Electronic Control of automatic Recloser
Electronic Recloser Contol is compromised of a number of programmable, solid solid-state electronic circuits that perform the command fuctions involved in automatic recloser operation. It is used to operate all electronically controlled reclosers.
the control panel of the control unit contains the programming and opening elements of the control.
Parts of the control panel of the electronic recloser:
Minimum trip resistors - Establish the minimum trip current levels for ground and each phase; cartridges are marked in primary amps and clamped in place.
Operation counter - record the cumulative trip operations of the control.
Sequence relay - steps the control through its operating sequence.
Ground- Trip Operation Switch -Blocks all ground in the BLOCK position: prevents unintentional tripping during single -phase switching operations.
Manual Control Switch - In the TRIP position, it locks out the control, advances the sequence relay lockout, and disconnects the battery from the control circuits. In the CLOSE position, it moves the sequence relay to the home position, reconnects the battery and closes recloser. If held in CLOSE position, it will override cold- load inrush ; however, the control will lockout for permanent faults.
Control Fuse- Protects the closing solenoid coil (on reclosers that employ solenoid closing) if closing voltage is too low. connected in series with the closing contactor in the recloser on motor- operated units; connected in series with the contactor rotary solenoid on reclosers that employ solenoid closing
Non- Reclosing Switch - Sets the control for one shot to lockout without disturbing the lockout setting of the operations selector.
Lamp Test Lockout Switch - Enables testing the signal lamp and checking for lockout.
Lockout Indicating Signal lamp - Provides visual indication of control lockout
Battery Test Tetminals - Enable checking battery voltage, charging rate ,and quiescent current drain.
Reset -Delay Plug - Determines the delay interval before the control resets after a successful reclosure during an operation sequence. the delay value is determined by position of the plug in socket adapter.
Phase Trip Timing Plugs - Provide a variety of current integrated timing curves on individual plugs for coordinating the phase trip operation with backup and downline protective devices.
Ground Trip Timing Plugs -Provide a variety of current integrated timing curves on individual plug for coordinating the ground-trip operation with backup and downline protective devices.
Reclosing Interval Plugs - Determines the delay interval for each closing operation. The delay value is determined by the position of the plug in the socket adapter. An instantaneous plug is available for the first reclose interval only.
Phase Trip Selector - Programs the number of fast phase trip operations as defined by the timing pug in Socket 1; the remaining (slower) operations to lockout are defined by the plug in phase trip socket 2
Lockout Selector - Programs the total number of operations to lockout.
Ground Trip Selector- Programs the number of fast ground trip operations as defined by the timing plug in socket 1; the remaining (slower) operations to lockout are defined by the plug in ground trip socket 2
the control panel of the control unit contains the programming and opening elements of the control.
Parts of the control panel of the electronic recloser:
Minimum trip resistors - Establish the minimum trip current levels for ground and each phase; cartridges are marked in primary amps and clamped in place.
Operation counter - record the cumulative trip operations of the control.
Sequence relay - steps the control through its operating sequence.
Ground- Trip Operation Switch -Blocks all ground in the BLOCK position: prevents unintentional tripping during single -phase switching operations.
 |
| Recloser Control panel |
Manual Control Switch - In the TRIP position, it locks out the control, advances the sequence relay lockout, and disconnects the battery from the control circuits. In the CLOSE position, it moves the sequence relay to the home position, reconnects the battery and closes recloser. If held in CLOSE position, it will override cold- load inrush ; however, the control will lockout for permanent faults.
Control Fuse- Protects the closing solenoid coil (on reclosers that employ solenoid closing) if closing voltage is too low. connected in series with the closing contactor in the recloser on motor- operated units; connected in series with the contactor rotary solenoid on reclosers that employ solenoid closing
Non- Reclosing Switch - Sets the control for one shot to lockout without disturbing the lockout setting of the operations selector.
Lamp Test Lockout Switch - Enables testing the signal lamp and checking for lockout.
Lockout Indicating Signal lamp - Provides visual indication of control lockout
Battery Test Tetminals - Enable checking battery voltage, charging rate ,and quiescent current drain.
Reset -Delay Plug - Determines the delay interval before the control resets after a successful reclosure during an operation sequence. the delay value is determined by position of the plug in socket adapter.
Phase Trip Timing Plugs - Provide a variety of current integrated timing curves on individual plugs for coordinating the phase trip operation with backup and downline protective devices.
Ground Trip Timing Plugs -Provide a variety of current integrated timing curves on individual plug for coordinating the ground-trip operation with backup and downline protective devices.
Reclosing Interval Plugs - Determines the delay interval for each closing operation. The delay value is determined by the position of the plug in the socket adapter. An instantaneous plug is available for the first reclose interval only.
Phase Trip Selector - Programs the number of fast phase trip operations as defined by the timing pug in Socket 1; the remaining (slower) operations to lockout are defined by the plug in phase trip socket 2
Lockout Selector - Programs the total number of operations to lockout.
Ground Trip Selector- Programs the number of fast ground trip operations as defined by the timing plug in socket 1; the remaining (slower) operations to lockout are defined by the plug in ground trip socket 2
Automatic Circuit Recloser
Recloser is a device that is used in over head distribution systems to interrupt the circuit to clear faults. Automatic reclosers have its electronic control senses and vacuum interrupters that automatically recloses to restore service if a fault is temporary. There are several attempts that may be made to clear and reenergize the circuit and if the fault still exist the recloser locks out. Reclosers are made in single-phase and three-phase versions, and use oil or vacuum interrupters.
Operation
Systems where a SCADA control interface capability is required in the use of automatic reclosers. The controls for the reclosers range from the original electromechanical systems to digital electronics. The operating sequence of all the reclosers can be all fast, all delayed or any combination of fast followed by delayed up. Fast operations clear temporary faults before branch circuit line fuses are weakened. Delayed operations allow time for down time protective devices to clear so that permanent faults can be confined to smaller sections of the system.
A complete electronic recloser package consists of the recloser which interrupts the circuit, an electronic control which senses over-currents and actuates the recloser and an interconnecting control cable.
Tripping and Closing
Operation
Systems where a SCADA control interface capability is required in the use of automatic reclosers. The controls for the reclosers range from the original electromechanical systems to digital electronics. The operating sequence of all the reclosers can be all fast, all delayed or any combination of fast followed by delayed up. Fast operations clear temporary faults before branch circuit line fuses are weakened. Delayed operations allow time for down time protective devices to clear so that permanent faults can be confined to smaller sections of the system.
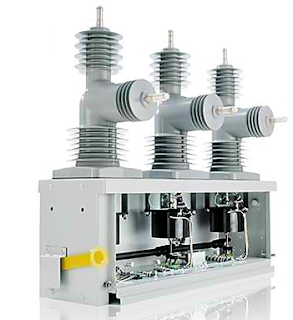 |
| Three Phase Vacuum Circuit Recloser image credit: www.abb.com |
Tripping and Closing
Recloser tripping and closing are initiated by signals from the
electronic control. When fault currents in excess of the programmed minimum-trip
value are detected in one or more phases, a signal from the control actuates a
low energy tripper in the operating mechanism of the recloser to trip the
opening springs and open the interrupter contacts. Closing energy and the force
required to charge the opening springs is supplied by a high-voltage closing solenoid
momentarily connected phase-to-phase through a high-voltage contactor. At the programmed reclosing time, the control
energizes a rotary solenoid in the operating mechanism which mechanically
closes the closing solenoid contactor to connect the closing coil to its power source. The energized closing coil pulls a plunger
down, charging the opening springs.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)

